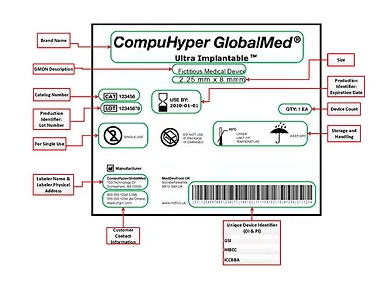
The U.S. FDA is now several years into its unique device identifier (UDI) program for medical device tracking. A number of other countries and regions have since been rolling out similar medical device tracking programs.
The goal of these programs is to improve safety, increase efficiency, and provide unambiguous accountability when it comes to control and tracking of medical devices and surgical instruments. RFID labeling has rapidly emerged as a viable solution for capturing UDI data in loaner systems as well as for the reprocessing of surgical trays.
UDI For Manufacturers Of Medical Devices
The FDA’s UDI program was developed to provide more accurate tracking of devices, speed up product recalls, and improve patient safety. Starting in 2014, different classes of devices are required to include a permanent mark containing a unique identifier and manufacturing information. The number of items that fall under UDI will be expanded each year through the 2020s.
Information on device labels are centrally managed via the Global Unique Device Identification Database (GUDID), making it available to stakeholders across the supply chain. In addition to improving safety, UDI helps manufacturers better manage and track inventory. Hospitals and other medical institutions could also use the UDI to manage and track surgical tray reprocessing as well as consignment inventory internally.
The UDI identification and information are encoded on the device using barcodes, direct part marking, or via RFID labeling. RFID tags are wireless, contactless, and long-range, making them particularly well suited for the automation of aspects of the Joint Commission’s Universal Protocol, as well as meeting FDA UDI requirements. They are designed to withstand the rigors of the hospital SPD environment, as well as harsh sterilization processes.
Medical device manufacturers use RFID tags to identify each device uniquely. More importantly, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning (like barcodes or direct marks would), so items can easily be scanned even when the UDI is not visible. The information collected can be shared with other stakeholders in the lifecycle and workflow of medical devices.
UDI In The European Union
The EU has matched the FDA regulations for its own UDI programs via the EU Medical Device Regulation 2017/745 and In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Regulation 2017/746. Compliance deadlines for different classes of medical devices in the EU will be rolled out through 2027.
UDI In Australia/New Zealand
Last year, the two countries released a new surgical asset tracking standard (AS/NZS 4187:2014) that mandated tighter regulations of reusable medical device reprocessing. Automation has been identified as the most efficient means of meeting the new standard. Hospitals will be moving from tray tracking instrument lifecycle tracking, with every stage requiring this type of tracking by December 2021.
UDI In China
The UDI program in China is focused on proving the authenticity of medical devices and identifying which devices are in the hands of a patient or medical staff/facility at any given time. In March, the CFDA released a draft of the UDI regulation for public comment, which included definitions of the UDI carrier that could include linear or 2D barcodes, as well as RFID or Near Field Communication (NFC) tags.
How to Capture UDI Data?
A recent report from Brick42 lays out the case for RFID in these applications quite well. By automating the identification, counting, and tracking of surgical instruments, an hospital SPD can deliver a high return on investment while also ensuring compliance with UDI rules in these regions.
The Xerafy Metal Skin® series offers high-performance on-metal RFID labels: durable, flexible, and long-range for precise asset and inventory management.
The award-winning labeling solutions have been co-developed with Fortune 1000 companies to deliver the ultimate labeling solutions for high-value items.
The benefits of RFID tracking can also be observed at hospitals that have deployed RFID surgical tracking systems with Xerafy. The company’s rugged RFID tags enable medical device RFID tracking to provide the visibility needed under these evolving UDI standards and requirements.
Xerafy is a pioneer in Industrial RFID, bringing to market several innovations that enable advanced industrial identification and automation capabilities.
In addition to a complete range of field-proven RFID tags available off-the-shelf, Xerafy offers Custom RFID Tags services, covering everything from a personalization service bureau to custom-design engineering capabilities.