NFC series
Near field communication devices for asset tracking and inventory management

With the Xerafy NFC series, technology meets cutting-edge design and durability.
The industry-grade NFC tags are crafted to enable asset tracking and inventory management in diverse environments.

“We love Xerafy’s range of special metal tags, which never let us down in any of our projects, especially for demanding production environments.”
NFC Tags That Stand Out
The NFC series of near field communication tags are engineered to offer tracking solutions optimized to perform in complex systems
Smartphone
Infrastructure-light technology
Battery-free
Long-life passive tracking devices
Durable
Designed for industrial durability
Read-Range
Combined with UHF RFID for longer range
Customization
Printed and encoded for unique identification
Cost-Effective
Solutions available for a variety of assets

RTI Outdoor NFC
Dual-Frequency For Asset Tracking
The RTI Outdoor NFC is a dual-frequency UHF+NFC tag designed for legacy tracking systems.
The durable tag is UV and IP68-proof and offers long-range performance in a nimble size.
Its dual frequency makes it perfectly suited for NFC tracking systems and for open-loop inventory management.

Circular TRAK NFC
Dual-Frequency For Consumer Applications
The NFC Circular TRAK is a dual-frequency UHF+NFC tag designed to power consumer-facing tracking applications.
The durable tag is wash- and detergent-proof and is designed to be used on metal containers.
With its dual-frequency, it enables new levels of tracking and interactivity for the circular economy.

Metal Skin® Titanium
25 NFC
Durable NFC Labeling
The Metal Skin® Titanium 25 NFC offers a durable NFC labeling solution for tracking applications where size is critical.
Designed for versatility, it operate s effectively on various surfaces with its industry-strength adhesive.
The printable label is ideal for high-value assets, including electronic devices, IT equipment, medical supplies. The Metal Skin® Titanium label combines a compact design with durable identification, ensuring precise and reliable asset tracking.
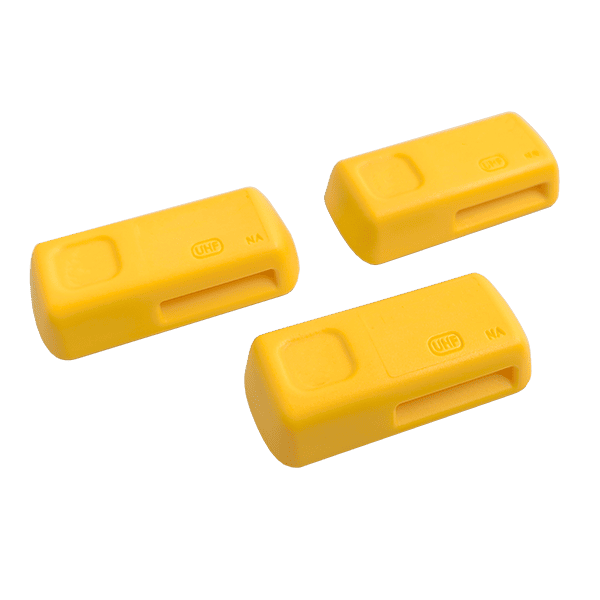

DUALBAND NFC
Dual UHF+NFC Durable Tag For Tubulars
The DUALBAND NFC is a durable dual-frequency UHF+NFC tag engineered for seamless identification and tracking of cylindrical industrial assets in Oil & Gas, Mining, Renewables, and Energy.
Designed for demanding field conditions, the DUALBAND NFC features slotted holes for secure banding onto industrial hoses, frac iron, lifting shackles, and high-pressure canisters. The dual-frequency capability supports long-range UHF RFID tracking while allowing mobile device interaction via NFC, enhancing field operations.
How to Print, Mark, Encode
The NFC Tags?
All tags in the NFC series can be fully
personalized to support the deployment of your tracking system
Silk-screen printing options include logo, serial numbers
Marking
Durable engraving with case color optimized for optical readability
Encode
User memory versions for
encoding and programming
Engineering
Custom options: Industrial adhesives, mounting systems...
Case Studies
Dual-frequency UHF+NFC industrial tags combine a consumer technology with an established industrial standard, to enable new tracking applications.
- RTI Management
- Circular Economy
- Oil and Gas
- Logistics
FAQs Asset Tracking with NFC Series
What is NFC (Near Field Communication)?
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a wireless technology that enables secure, contactless communication at short range with low energy consumption.
It is particularly suitable for asset tracking due to its reliability, ease of use, and compatibility with smartphones and other NFC-enabled devices.
NFC operates using standardized protocols, ensuring consistent performance across a wide range of industrial applications:
– ISO/IEC 14443 A
– ISO/IEC 14443 B
– JIS X6319-4
For more, see: https://nfc-forum.org/
What are NFC tracking applications and uses?
NFC was initially developed with consumer applications like contactless payments (e.g., Apple Pay, Samsung Pay), transport, and ticketing in mind.
However, its applications have expanded into industrial use, particularly in Industry 4.0 and IoT:
+ Industrial asset tracking and management
+ Production line visibility and quality control
+ Tracking of returnable transport packaging such as LPG cylinders
+ Tool and equipment tracking in construction and maintenance projects
+ Access control, user identification, and attendance tracking


NFC vs RFID: Key differences for asset tracking
NFC devices operate at the same frequency as high-frequency RFID, readers and tags — 13.56 MHz. It can therefore be seamlessly integrated into an existing HF RFID infrastructure.
Unlike UHF RFID, which has a read range of up to 20 meters and can read hundreds of tags simultaneously, NFC works at very short distances (typically 10 centimeters) and uses two-way communication.
This makes NFC ideal for precise, secure asset tracking, allowing assets to provide real-time status or condition feedback. NFC is particularly useful in environments where targeted interaction with individual assets is critical.

What types of NFC tags are available?
There are several types of NFC tags used for asset tracking and inventory management, each with its own features and capabilities.
Xerafy provides both NFC tags and hybrid dual-frequency NFC+UHF tags, offering flexibility for different asset tracking requirements.
When selecting NFC tags, factors to consider are the type of assets to track, the environment they are in, any specific requirements for data storage capacity or security, as well as compatibility with the tracking system deployed.
NFC Stickers: Disposable adhesive labels with an embedded NFC chip, easily attached to assets such as equipment or documents, or as labels for larger assets and packaging.
NFC Tags: Robust devices with a sturdy outer shell that safeguards them against washing, shocks, and UV exposure, ensuring reusability. They come with multiple mounting options and are scalable and durable for asset tagging.
NFC Metal Tags: Designed specifically for use on or near metal objects, similar to metal RFID tags, providing reliable performance in metal-intensive industrial environments.
NFC Cards: Plastic cards with embedded NFC chips, often used for access control but also applicable for asset tracking.

NFC chips are the integrated circuits (ICs) that power NFC tags, making them essential for asset tracking. They are passive components, meaning they draw power from an NFC reader through magnetic induction, similar to UHF RFID chips.
Modern NFC chips are designed to support a wide range of applications, including tamper detection for sealed products and condition monitoring, such as moisture sensing. Leading manufacturers of NFC chips include NXP, EM Microelectronic, Texas Instruments.
The evolving capabilities of these chips enable more advanced tracking and monitoring solutions, enhancing the utility of NFC for asset management.
Are NFC and HF RFID the same when it comes to industrial asset tracking?
Yes, for most practical purposes in industrial applications, NFC and HF RFID can be considered functionally equivalent.
Both operate at 13.56 MHz and follow the same global standards (ISO/IEC 14443, ISO/IEC 15693, and ISO/IEC 18092), which ensures interoperability across tags, readers, and mobile devices.
In asset tracking use cases, the choice between “HF” and “NFC” usually reflects the interface: HF refers to industrial-grade readers, while NFC typically refers to smartphone-based interactions.
Key characteristics of both include:
Short read range: Typically from a few centimeters to 1 meter, ideal for close-proximity identification and secure access.
Slower data transfer than UHF, but sufficient for item-level interactions.
Susceptibility to metal and liquids, although mitigated with proper shielding and tag design.
With the rise of dual-frequency tags like those in the Xerafy NFC Series, businesses can now combine the long-range, high-speed capabilities of UHF with the convenience and accessibility of NFC, enabling new workflows such as:
+ Smartphone-based spot checks and updates
+ Operator interactions without special equipment
+ Field verification where UHF infrastructure is not available
These dual-frequency tags are especially useful in asset tracking scenarios that benefit from both system automation (UHF) and manual access (NFC).
Can RFID readers read NFC tags?
Yes, a High Frequency (HF) RFID reader can directly read NFC tags because they both operate at 13.56 MHz.
Some UHF readers (RAIN RFID), such as the Apulsetech α811 UHF RFID Reader have an NFC mode and a designated NFC reading area.
How to read NFC tags with a phone?
NFC tags can be read with any phone that supports NFC functionality.
For iOS devices:
All models since the iPhone X support NFC via the in-app NFC button.
The NFC reader is located near the top of the device.

For Android devices:
To check if your phone supports NFC and enable it, follow these steps:
Go to “Settings” on your Android device
Select “Connected devices” or “Connections”
Look for “NFC” (and sometimes “Android Beam”)
Turn on “NFC” and “Android Beam” if available
The NFC reader’s location varies by model. To find it, press and hold the NFC icon in the settings menu, and the location of the reader will be shown on the screen.
Once you’ve confirmed your phone supports NFC and identified the location of the NFC reader, follow these steps to enable NFC scanning:
Turn on NFC in your phone settings.
Know where the NFC reader is located on your device.
Remove any accessories, especially those containing metal, as they may interfere with the scan.
Hold your phone’s NFC reader near the NFC tag or sticker for at least 1 second.
Note: A weak internet connection can cause scanning errors. Ensure your phone is connected to the fastest network available to avoid connection dropouts.
If the phone isn’t reading NFC tags automatically, an NFC app to help with reading. The following options can be found in the App Store or Google Play: NFC TagInfo, NFC Tools, NFC Reader.



How to encode / write NFC tags?
NFC tags can be encoded (written to) with information useful for asset tracking, inventory management, automation, or sharing information.
With a phone:
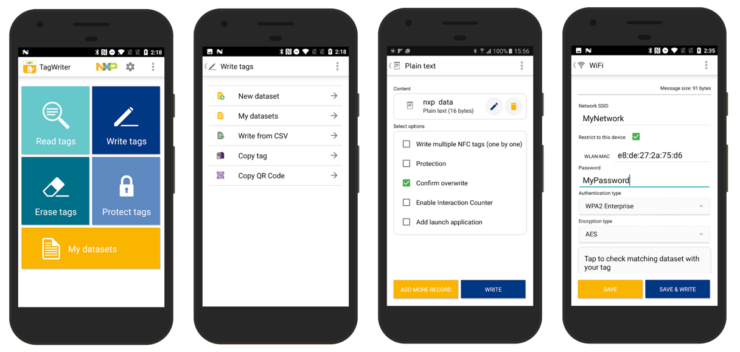
- Install an NFC tag writing app, such as NFC TagWriter or NFC Label Tool.
- Follow the app’s instructions to encode the NFC tags.
With an RFID reader:
Use an HF reader along with compatible software to read and encode NFC tags:
Install the appropriate software for your HF reader on your computer.
Ensure the software is compatible with your reader model.
Place the NFC tag on the HF reader for optimal scanning.
Use the software to read, process, and import the data into your system.

Xerafy’s service bureau can handle the encoding of NFC tags. This service allows tags to be pre-configured with the required data, which ensures consistency and saves time during deployment. This can be particularly useful in large-scale applications like asset tracking or inventory management, where manual encoding would be impractical.