RFID Tags
For
Tools
Pallets
Assets
Parts
Drill Pipes
Totes
IT Assets
Inventory
Surgical Trays
Advanced RFID tagging solutions co-developed with Fortune 500 companies to tackle the challenges of asset tracking, inventory management, and supply chain visibility

Xerafy’s tagging solutions are engineered to deliver precision and durability for specialized asset identification and tracking systems:
RUGGED
Benchmark-Leading Performance and Reliability
TRAK
Durability for Returnable Assets and Inventory
SKIN
Smart Labels for Enhanced Supply Chains
IOT
Advanced Devices for Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
Companies all over the world trust Xerafy for their critical tracking systems:
























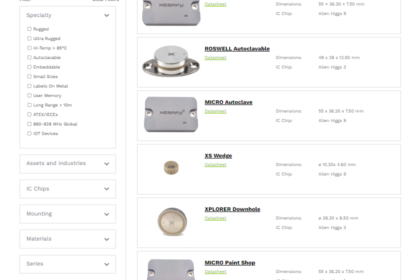
Select Your Tags
Find the right tags for your assets and applications, or filter by Specialty, IC Chip, Mounting System, and Material
FAQs RFID Tags
How to choose the right RFID tag for a specific project?
To select the best RFID tags for a tracking system, consider the following factors:
- Asset Type and Environment: Identify the material of the asset (metal, plastic, etc.) and the environmental conditions it will face (e.g., temperature, chemicals, sterilization).
- Durability: If you’re working in extreme conditions, rugged tags (e.g., MICRO, ROSWELL) might be necessary. For more versatile or customizable solutions, durable tags like the TRAK series, or printable RFID labeling solutions may be ideal.
- Industry: Ensure your RFID tags meet specific compliance standards, such as ATEX/IECEx for hazardous environments or FDA/UDI for healthcare.
Visit the Xerafy Product Selector for detailed product options, and refer to the Tagging best practices.
Xerafy also offers industry-specific RFID tagging solutions, co-developed with Fortune 500 companies, to meet the precise asset and application needs across industries such as MRO, Oil and Gas, Healthcare and Manufacturing (see RFID Tracking Application Guide for a full list).
Personalized consultations with the Xerafy Engineering Team are available to ensure the tags are aligned with the specific application requirements. Additionally, Xerafy provides full deployment support, from testing to Proof of Concept (POC), facilitated by our network of Authorized Partners.
What environmental conditions can Xerafy RFID Rugged tags withstand?
Xerafy RFID rugged tags are engineered for harsh environments and undergo rigorous testing to ensure optimal performance. These tags can withstand:
1. High/Low Temperature Cycling: Tags like the ROSWELL and MICRO Paint Shop can cycle up to 250°C, making them ideal for industrial processes or autoclave sterilization.
2. Chemical Exposure: With protective casings, models like MICRO Industrial, MICRO Power, and NANO Plus resist harsh chemicals and solvents.
3. Water & Moisture: IP65, IP67, and IP68 rated tags provide dust, water, and moisture protection.
4. Performance on Metal Surfaces: On-metal tags, such as MICRO and PICO, deliver reliable reads even in metal-rich environments like MRO and industrial manufacturing.
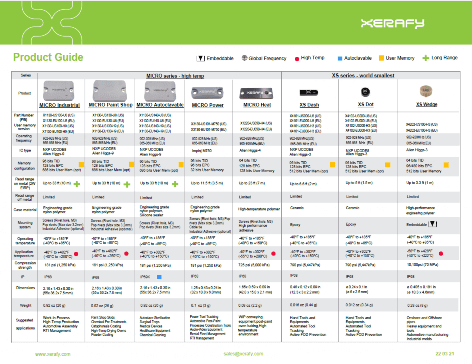
For more detailed environmental testing results, check individual datasheets or the Product Guide for a side-by-side comparison.
Which standards are Xerafy RFID tags compatible with?
All Xerafy RFID tags comply with key industry standards to ensure compatibility with various readers, tracking systems and software. Key certifications include:
+ UHF RFID Compliance: RAIN RFID, ETSI, and FCC compliant for global use.
+ ISO Standards: ISO 18000-6C and EPC Class 1 Gen 2 ensure cross-platform integration.
+ Industry-Specific: ATEX for explosive environments, VDA for automotive, FDA/UDI for healthcare.
+ Safety and Environmental Compliance: All Xerafy tags are RoHS and CE compliant, ensuring safety and sustainability.
What are the memory options for Xerafy RFID tags?
Xerafy RFID tags offer flexible memory options depending on the RFID chip featured, for various data storage needs:
+ EPC Memory: 96 bits, extendable to 512 bits for unique identifier storage.
+ User Memory: Up to 512 bits for product codes, serial numbers, and other key asset details.
+ TID Memory: A 64-bit TID for unique tag identification, enhancing security and anti-counterfeiting measures.
These options allow for tailored solutions across different industries, from asset management to supply chain traceability. For more details, check individual datasheets or the Product Guide for a side-by-side comparison.
How does Xerafy ensure the long-term reliability of its RFID tags?
Our RFID tags, especially those in the Xerafy RUGGED series, undergo rigorous qualification in the field. Thanks to their industry-grade durability, reliability, and consistency, they are often noted for outliving the assets they track.
Materials and engineering requirements are defined based on industry preferences to ensure each tag is suited for its specific application. Full control over the entire design and manufacturing process allows the implementation of advanced techniques that enhance tag durability. The company maintains stable product lines which enables ongoing enhancements with each version.
By combining these elements, Xerafy RFID tags deliver benchmark-topping performance and reliability, providing long-term value in a wide range of industrial applications.
What warranty and support options does Xerafy offer for its RFID tags?
Xerafy provides full warranty and support options for our RFID tags and labels, ensuring reliability and customer satisfaction. Each product comes with a specific warranty period, which covers defects in materials and workmanship. Detailed warranty information is available on the datasheet for each product.
For direct support, troubleshooting assistance, or additional information about our warranty terms, our dedicated Sales representative is ready to help.
What customization options does Xerafy offer for RFID tags?
Yes, Xerafy RFID tags can be fully customized to meet the specific needs of your application, particularly in industrial asset tracking systems. Here’s how we can tailor our tags:
1. Printing:
– The Xerafy Service Bureau offers the option to print and laser engrave logos, serial numbers, or other identifying information directly onto the tag, ensuring the assets are clearly marked and easily identifiable.


2. Data Encoding:
The Service Bureau can encode tags with specific data, such as unique identifiers, product codes, or other relevant information, ensuring seamless integration into your tracking system from day one.
3. Material and Design:
Tags can be engineered in various materials and designs, including on-metal, high-temperature, and autoclavable options, to ensure they meet the environmental demands of your application.
4. Frequency and Memory:
Tags can be engineered to different frequency ranges and memory capacities, depending on the specific requirements of your project.
For more details on customization options or to discuss specific needs, feel free to reach out to our Engineering Team or explore our service bureau offerings.
What are the best practices for RFID tag placement to optimize read accuracy?
For optimal RFID tag placement and enhanced read accuracy, it is essential to consider the type of assets being tagged and the specific environment in which they operate. Tags should be placed on a flat, clean surface away from metal or liquids, which can interfere with signal transmission. Additionally, ensure that the tag orientation aligns with the direction from which it will be scanned most frequently.
For detailed guidelines on achieving the best read rates and avoiding common placement errors, please refer to the Xerafy engineering team’s comprehensive guide on RFID tagging.
Can Xerafy RFID tags be used in medical autoclaves or sterilization processes?
Yes, Xerafy RFID tags can be used in medical autoclaves or sterilization processes.
The MICRO Medical, MICRO Autoclavable and ROSWELL Autoclavable are specifically engineered for the healthcare industry, capable of withstanding rigorous cleaning and sterilization procedures without losing functionality.
These tags ensure reliable performance through repeated reprocessing cycles, making them ideal for tracking instruments and equipment in sterile environments. This durability supports effective asset management and compliance with health safety standards.
How do Xerafy on-metal RFID tags perform in industrial environments?
Xerafy’s MICRO, PICO, XS and ROSWELL series are on-metal RFID tags specifically engineered for peak performance in industrial environments, including those prevalent in Manufacturing, MRO and Oil and Gas.
These tags are designed to maintain functionality and deliver reliable read ranges even when mounted directly on metal surfaces. The robust construction of our on-metal tags ensures they withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, vibrations, and potential chemical exposures, making them an ideal choice for tracking assets that are subject to strict operational demands.
How does metal-mount RFID differ from regular tags?
Metal RFID tags are different from regular RFID tags as they are specifically designed to perform optimally when attached to metal objects.


Metal presents challenges for regular tags and will impact their performance:
- Metal surfaces reflect, scatter, or absorb RF signals, which can interfere with the performance of the RFID system.
- Metal objects can also detune the RFID antenna, which can cause the system to fail.
Metal RFID tags have unique antenna designs and materials and a special shielding layer that helps minimize interference from the metal surface and prevent the detuning of the tag’s antenna.
These tags typically have a thicker substrate than regular RFID tags, which helps protect the tag from damage.
What options does Xerafy offer for embedding RFID tags?
Xerafy offers tags that can seamlessly embed into the metal or plastics of equipment and assets, providing durable and reliable performance.
The PICO In, XPLORER and XS Wedge tags, for instance, can be flush-mounted into metal. This asset-tagging method provides additional protection that is particularly suited for the most challenging applications industries such as Oil and Gas and Manufacturing.
Embeddable tags have a special design that allows them to work effectively despite being flush mounted in metal. These tags are typically smaller and thinner than on-metal tags, which makes them easier to embed in metal objects.
Similarly, RFID tags can be injection molded into the plastic of a tool handle or a plastic bin by the manufacturer, turning them into Connected Assets.
What are the maximum temperatures for RFID tags?
Industrial RFID tags are specifically engineered to operate within a wide temperature range to withstand harsh environments, with maximum temperatures depending on the specific type of the tag.
Xerafy’s industrial RFID tags can typically reach 70-85C, with specialty products going higher:
250C – ROSWELL series for Oil and Gas industry, MICRO Industrial and Paint Shop for Manufacturing
230C – XSKIN Theta for injection molding
220C – XS Wedge
200C – MICRO Heat
It’s also worth noting that while some RFID tags can withstand high temperatures, they may not function optimally at these extreme temperatures.
To ensure reliable and accurate performance, it is recommended that RFID tags be specifically designed and tested for the temperature range of the intended application.
What is the difference between operating and survival temperatures?
Operating temperature: The temperature range where the tag can read and write data reliably.
Operating temperatures typically fall within a specific range, such as -40°C to +85°C for certain passive UHF tags.
Survival temperature: The maximum temperature the RFID tag can withstand without sustaining physical damage.
Think of it as the tag’s tolerance for short-term exposure to extreme heat.
Survival temperatures are generally higher than operating temperatures. Exceeding them can lead to malfunctions, data errors, or even permanent damage to the tag’s internal components.