RFID Tagging 101
Hands-On Guide from the Xerafy Engineering Team for Efficient RFID Retrofitting of Assets and Inventory
Retrofitting assets with RFID tags is a critical step toward enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy. Engineers face numerous challenges during this process, from integrating with legacy systems to managing diverse environmental conditions. This guide, prepared by the Xerafy engineering team, offers a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to RFID tagging, designed to address these challenges head-on.
Built on hands-on experience from across a range of industries, this guide highlights best practices for successfully implementing RFID technology. Whether you’re dealing with tools, drill pipes, hospital equipment, manufacturing machinery, medical devices, or returnable containers, the following six steps will equip you with the insights needed to overcome obstacles and achieve optimal system performance:
The structured methodology ensures that every aspect of RFID tagging is addressed, resulting in a successful deployment. With detailed insights rooted in practical engineering experience, this guide serves as a technical resource for those looking to optimize asset management through RFID technology.
6 Steps To Successful RFID Tagging
Selecting the right RFID tracking solution is a critical process. Xerafy’s 6-Step ABCDEF approach provides a clear framework to define and meet the essential performance requirements for any application.
What Assets Does the RFID System Track?
Standardized and proven RFID tagging solutions are available for the most common types of assets. Other key selection factors include the materials of the assets, their criticality to operations, their value, and the potential return on investment from improved tracking.
Tools, heavy machinery, returnable containers, and medical devices benefit from established tagging technologies that are optimized for reliable performance. Xerafy’s metal tagging solutions, for instance, leverage the presence of metal in assets to enhance RF performance, ensuring precise tracking even in the most challenging environments.
Metal is the most common material in industrial applications, followed by plastics, with other materials such as wood, glass, and cardboard also in use. Each material presents specific challenges: for example, wood and cardboard may absorb moisture, impacting tag performance, while glass can cause signal reflection. To overcome these obstacles, specialized RFID tags are designed to ensure optimal performance across different substrates.
RFID tags are typically applied to the surface of the asset, and both the composition of the substrate and the nature of the asset’s contents can significantly influence the tracking system’s effectiveness—affecting factors such as read range, accuracy, and durability.
Durability is another critical consideration in RFID tagging, particularly in industrial settings. Xerafy’s rugged RFID tags are engineered to withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, impacts, and chemical exposure. These tags are built for long-term reliability, maintaining consistent performance even under the most demanding circumstances.
Choosing the Optimal Bonding Method for Your RFID System
Determining the most appropriate bonding method for RFID tagging involves assessing several critical factors influencing durability, operational performance, and return on investment (ROI).
Each industry has its bonding methods of choice, such as rivets, screws, welding, adhesives, epoxy, magnets, Velcro, cables, and zip ties. Key considerations here include:
- The cost and speed of the bonding method
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to impacts, temperatures, humidity, or chemicals
- The lifespan of the asset
- The anticipated rate of tag attrition
- The need for RFID tags to be reusable and replaceable
When considering bonding methods, it’s also essential to weigh the choice between adhesive labels and hard tags. Adhesive RFID labels are ideal for applications where flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of deployment are priorities, especially on flat or slightly curved surfaces like cardboard boxes or plastic containers.
However, in harsher environments, where durability and long-term reliability are critical, hard tags come with more rugged bonding options. Xerafy’s expertise in advanced tracking systems has led to the development of RFID tagging solutions that can be secured using epoxy glue, welding, or embedding directly into plastics and metal.
Xerafy’s embeddable RFID tags involve securely installing the tag by screwing it into a cavity or sealing it within the asset, providing enhanced durability and reliability, even in the most challenging environments.
How Much Customization is Required for the RFID System to Be Deployed?
Standardized RFID tags offer a strong foundation. The ability to customize them enhances their effectiveness, especially when dealing with unique asset types or industry requirements.
On-site or supplier-based customization options include:
- Printing and Encoding: RFID tags can be printed with human-readable information and encoded with asset-specific data, providing an immediate reference for workers and systems alike. This is particularly useful in environments where both RFID scanning and visual identification are needed.
- Laser Engraving: For applications requiring durability, laser engraving offers a permanent, tamper-proof method to mark RFID tags. This is ideal for harsh environments where printed information may wear off over time.
- Hybrid RFID Tags: Combining RFID with optical information, such as barcodes or QR codes, provides flexibility in how data is accessed. This approach is useful in scenarios where both RFID readers and traditional barcode scanners are used.
- RFID Tuning: Customization can extend to the tuning of RFID performance to prevent stray reads in a high-density environment such as a data center or account for frequency shifts in challenging downhole operations.
Xerafy UHF labels, in particular, can be supplied blank, ready to be printed and encoded on-site using leading industrial RFID printers like Zebra, SATO, Toshiba, Printronix, and Postek. Alternatively, Xerafy’s service bureau can help customize tags to your precise specifications, whether through advanced printing, encoding, or laser marking.
How is Data Stored in the RFID System?
RFID tracking systems reliably identify assets using the information stored in the memory of RFID tags. Increasingly, these systems rely on tags that store only an asset identification number, with comprehensive information stored in the cloud.
RFID chip memory types used for asset identification include:
- TID Memory (Tag ID): A unique, unchangeable serial number assigned to each chip, serving as a permanent identifier.
- EPC Memory (Electronic Product Code): This memory type functions like an electronic barcode and can be reprogrammed, password-protected, or permanently locked, offering flexibility for various applications.
- Extended User Memory: For applications that require more extensive data storage, such as complete records or encrypted information, some RFID chips offer extended user memory. This is particularly useful in environments with limited cloud coverage or where offline access is essential.
Various industry requirements, such as VDA in Automotive and some retail mandates, come with higher memory requirements. Xerafy supports these needs by offering RFID chips with extended user memory from industry leaders like Impinj, NXP, and Alien Technologies, ensuring robust performance in even the most demanding conditions.
What Are the RFID System's Environmental Conditions?
From disposable labels to durable tags and rugged solutions, RFID tags are available in a variety of form factors tailored to withstand the specific environmental conditions under which the system will operate.
Identifying these conditions is critical to ensuring the RFID solution’s long-term survivability and reliability. Key environmental factors to consider include:
- High Temperatures: Can the tags endure high temperatures? There are rugged tags designed to survive most industrial processes and even the rigors of downhole drilling.
- Temperature Cycling: How well do the tags perform under rapid temperature changes, such as transitioning between high temperatures and ambient environments?
- Shocks and Vibrations: Are the tags resilient to mechanical stresses? Tags with metal housings are often used with moving vehicles or heavy machinery.
- Moisture or Immersion: Can the tags operate effectively in wet conditions or even when fully submerged? Tags with high IP ratings offer reliable performance in such environments.
- Exposure to Caustic or Acidic Fluids: How resistant are the tags to harsh chemicals? Selected materials can provide the necessary protection to operate in hospitals, MRO shops, or industrial environments for instance.
- Indoor vs. Outdoor Operations: Are the tags suitable for outdoor use, where they may face exposure to weather elements like UV radiation, rain, heat and cold?
- Industry Standards: IP ratings for water and dust resistance or ATEX certification for explosive environments further ensure the tags’ reliability in demanding conditions.
Some application environments present particularly complex challenges. For example, an automotive paint shop requires RFID tags that can withstand extreme heat, chemical exposure, and high moisture levels. Xerafy leverages its extensive application expertise to offer sector-specific tagging solutions that address these unique challenges, delivering innovative RFID tracking technology tailored to the most demanding industries.
Where to Place the Asset's Tag for Optimal System Performance?
The size and shape of the tag must align with the available space on the asset, taking into account the asset’s surface, curvature, and location to ensure reliable performance and optimal usability.
While RFID tags come in a wide range of sizes and shapes, RF performance is often linked to the overall tag size, with larger tags typically offering better performance. However, the choice of tag and its placement must also consider the following factors:
- Surface Curvature: Metal tags placed on curved surfaces may experience reduced performance if not properly aligned. Flexible or conformable tags can be used to maintain RF integrity on non-flat surfaces.
- Space Constraints: In situations where space on the asset’s surface is limited, compact tags that maintain high RF performance are essential.
- Workflow and Usability: Tags should be placed in locations that align with the workflow, ensuring they are easily readable by RFID readers without disrupting operations. Considerations include tag orientation relative to the reader and minimizing potential signal interference from nearby objects or assets.
Xerafy’s portfolio of RFID tags is engineered to overcome these challenges, offering solutions that provide outstanding performance in even the smallest and most rugged form factors. By breaking through the traditional size/performance limitations, Xerafy ensures that tags can be effectively placed on assets of various shapes and sizes without compromising system efficiency.
FAQs RFID Tagging
What are Connected Assets?
Retrofit challenges can be addressed by engineering RFID and IoT features directly into products, transforming them into Connected Assets without compromising design or performance.
The expertise of Xerafy’s engineering team supports Fortune 1000 companies in enabling real-time data sharing and tracking within their complex, connected ecosystems. This approach ensures long-term performance and adaptability, effectively future-proofing their operations.
What RFID tagging solutions are best suited for tools?
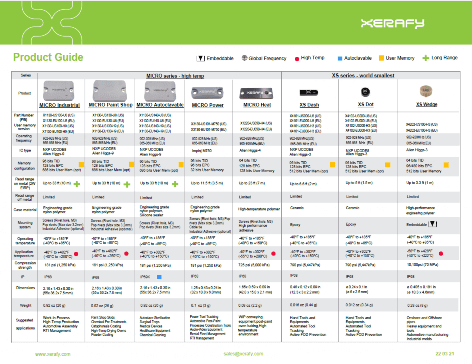
For tool tracking, Xerafy offers rugged, compact RFID tags like the Xerafy PICO series. These tags are designed to withstand harsh conditions and provide reliable performance in small form factors, making them ideal for managing hand tools and other equipment in demanding environments.
Which RFID tags are best for metal assets?
Xerafy’s metal tagging solutions, such as the Xerafy METAL SKIN labels and MICRO series, are engineered specifically for metal surfaces. These tags leverage the presence of metal to enhance RF performance, ensuring accurate and reliable tracking even in challenging industrial environments.
What RFID tags are recommended for returnable assets like pallets and RTP?
For tracking returnable assets like pallets and Reusable Transport Packaging (RTP) and RTI, Xerafy offers the TRAK, POD and OUTDOOR series.
These durable RFID tags are designed to withstand repeated use, rough handling, and exposure to the elements, ensuring consistent tracking and inventory management over time.
What RFID solutions does Xerafy offer for tracking weapons?
For weapon tracking, Xerafy provides compact RFID solutions like the Xerafy XS series and PICO series. These tags are designed to be discreetly embedded or attached to firearms, offering secure and tamper-proof tracking for military and law enforcement applications.
Can RFID tags be embedded into assets?
Yes, Xerafy specializes in embedding RFID tags directly into assets, allowing for seamless integration into the asset without compromising its structure or function.
The Xerafy PICO In, XS Wedge and XPLORER are all engineered to be embedded in metal, while the XSKIN Theta can be embedded into plastics using injection molding.
How to RFID tag concrete surfaces?
For concrete surfaces, Xerafy offers the Cargo OUTDOOR and the ROSWELL, which are designed to be mounted on or embedded in concrete. These tags are built to withstand the harsh conditions of construction sites and industrial environments, providing reliable tracking for concrete assets.