The end-user is a leading aerospace manufacturing company specializing in the production of composite aerostructures. The end-user decided to remain anonymous to maintain confidentiality and safeguard proprietary manufacturing processes and operational strategies. As a leading player in the aerospace industry, the company prioritized protecting its competitive edge while sharing insights into the RFID implementation journey.
Autoclave processes are central to composite manufacturing, playing a critical role in curing composite materials under high temperatures and pressure to meet stringent aerospace quality standards. Work-in-process tracking within these autoclave operations posed significant challenges, necessitating innovative RFID solutions.
This case study summarizes insights from an original presentation by Jim Morgan, published by RFID Journal (All rights reserved to the original source).
Operational Challenges in Composite Manufacturing
The company faced significant challenges in scaling its production processes to meet aggressive delivery timelines for commercial aviation growth programs:
Inefficient Tracking: Labor-intensive and inaccurate tracking of tooling, materials, and parts led to frequent disruptions in workflows.
Poor Location Accuracy: Low fidelity of item location caused delays and inefficiencies in inventory and production management.
Error-Prone Documentation: Manual data entry increased the likelihood of errors, compromising documentation accuracy and traceability.
Integration Complexities: The integration of tracking systems with MES, ERP, and shop floor control required advanced technical planning to ensure seamless data flow.
Asset Utilization Challenges: Inefficient asset tracking resulted in underutilization of high-value tools and materials, affecting production timelines.
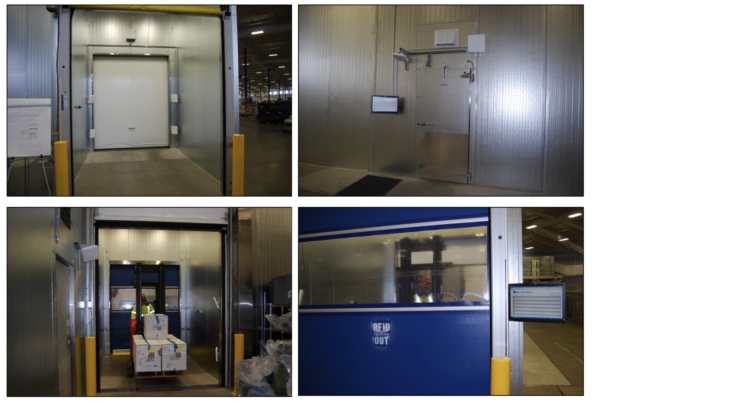
The operational challenges were intensified by the unique conditions of composite aerostructures manufacturing. Freezers play a critical role in preserving prepreg materials by preventing premature curing, while autoclaves apply extreme temperatures and pressure to cure composites to the required specifications. These environments necessitate meticulous tracking to maintain quality and ensure compliance. Specifically, autoclave processes required precise monitoring of WIP to document curing cycles accurately and minimize production delays.
With a need for automation and precision, the company embarked on a facility-wide RFID project.

RFID Implementation and Technical Solutions
The aerospace manufacturer implemented an RFID solution to address both process-specific and operational challenges, ensuring precision in composite manufacturing.
This system was designed specifically to address WIP challenges, automating the tracking of composite materials, tooling, and WIP across critical production stages, including autoclave curing and freezer storage, ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace standards.
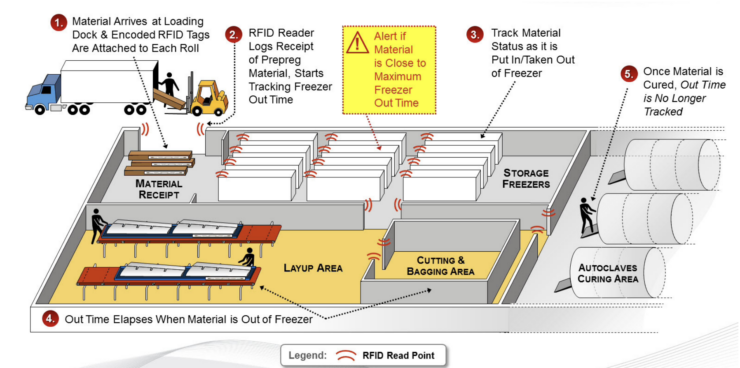
The deployed tracking system consisted of:
Asset Tracking Tags: They ensure durability and reliability in extreme conditions, essential for maintaining production quality and compliance. Xerafy MICRO high-temperature tags were selected for tracking during the autoclave curing process for their ability to survive repeated cycling.
MICRO series – High-reliability RFID tags for asset tracking in complex processes: Resistant to High Temperatures, Shocks, and Chemicals
4×4 RFID labels were used for monitoring composite materials stored in cold environments, with an AS3 freezer-grade adhesive. On-site printing allowed for immediate customization and rapid labeling, ensuring the tracking system could adapt to operational demands without delays.

Readers: The deployment included 115 Impinj Speedway R420 RFID fixed readers, complemented by 460 Impinj far-field antennas, and Motorola MC9090-Z handheld readers.


RFID Software: Provided by OATSystems, a division of Checkpoint Systems. The asset tracking software is integrated with the manufacturer’s MES, ERP, and reporting systems.
A pilot project was initially conducted to validate the system in a real-world environment. According to Jim Morgan, “This project has demonstrated that RFID can be scalable and address many inefficiencies, making it an essential part of our manufacturing process moving forward.”
Operational Benefits and Outcomes
The solution automated key processes, including inventory management, production tracking, and documentation. It reduced manual labor and improved accuracy, enabling the manufacturer to meet aggressive delivery timelines while maintaining high-quality standards.
Improved Manufacturing Efficiency: Automation led to faster production cycles, helping meet delivery timelines.
Visual Factory Integration: RFID contributed to operational visibility by mapping metrics and creating a human-machine interface (HMI).
- Enhanced Asset Utilization: Increased accuracy in tool, material, and part inventory tracking improved utilization rates.
Reduced Waste and Errors: Automated data capture minimized manual entry errors, improving product traceability and documentation.
Operational Focus: Employees were able to focus on value-added tasks rather than spending time locating tools, materials, and instructions.
Customer Satisfaction: Better process tracking and product quality improved client confidence and satisfaction.
The scalable design ensures it can support future aerospace programs, facility expansions, and integration with evolving manufacturing technologies.
Best Practices for Manufacturing RFID Systems
Tag Selection and Testing: RFID tag selection is critical and time-consuming due to variations in tag design, performance, and material suitability. Sufficient time for testing and order placement should be factored into the project timeline.
Tag Placement Matters: Careful consideration must be given to tag placement, particularly on conductive materials that can block or reflect radio frequency energy. Proper tag positioning is essential to ensure optimal read rates.
Reader and Antenna Placement: Antenna positioning must be planned in the context of the workspace to avoid interference with operations while ensuring full coverage.
Enterprise System Integration: RFID system integration with existing enterprise systems such as MES and ERP adds complexity. Advanced planning and flexibility in adapting the Auto-ID system are critical for successful implementation.
Xerafy is a pioneer in Industrial RFID, bringing to market several innovations that enable advanced identification and automation capabilities in manufacturing.
In addition to a complete range of field-proven RFID tags available off-the-shelf, Xerafy offers Custom RFID Tags services, covering everything from a personalization service bureau to custom-design engineering capabilities.











