RFID Readers 101
The Xerafy engineering team’s guide to handheld UHF RFID readers for asset tracking and inventory management
Incorporating an RFID tracking system is a pivotal step for any business. At the heart of such a system are industrial RFID readers, which serve as a crucial component, facilitating communication with tags and granting access to their data.
When integrated into the right RFID system, a UHF RFID reader can identify assets quicker, more accurately, and at a reduced overall cost at various points of the asset’s lifecycle.
This guide, put together by the award-winning Xerafy engineering team, focuses on handheld readers that operate within the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) range, specifically between 840 MHz and 960 MHz, and are designed in accordance with GS1’s EPC UHF Gen2 air interface protocol.











What is an RFID Tracking System?
An RFID UHF tracking system is a type of radio frequency identification system that operates in the ultra-high frequency range.
This system employs UHF tags, which utilize electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. The UHF frequency range typically operates between 860 and 960 MHz, enabling long-range communication between the tag and reader.
UHF RFID tracking is versatile and is used in a variety of applications, including inventory management, supply chain optimization, and RFID tracking system for manufacturing. These industrial RFID systems are highly efficient, allowing for quick and accurate data collection, and can significantly enhance the overall efficiency and productivity of a business.
What are the types of UHF RFID readers available?
There are different types of UHF RFID readers available, including wireless RFID readers, mobile RFID readers, UHF fixed readers, portable RFID readers, handheld RFID readers, integrated RFID readers, and USB readers.
Industrial readers usually come as either handheld devices or as stationary units attached to a piece of equipment (ceiling, gate, chokepoint etc). When tracking assets and inventory, a hybrid approach of utilizing fixed and handheld RFID readers is commonly employed.
Key differences to consider between the two types of readers include: read speed, read range, and overall efficiency of the tracking system.

A fixed reader is better suited for continuously reading tags, for applications where items move through a fixed point. Also, fixed readers have a higher read range and can read a large number of tags on the go. Being mounted in a fixed location, they can be used to track items as they move through a specific area, such as a warehouse or production line.

Handheld RFID readers, on the other hand, are more like micro-computers. They run on rechargeable batteries with rugged versions available for industrial environments and mobile phone plugins. They can often also scan barcodes, offering a versatile solution for spot checks, with a screen for direct reading and data input.
Compared to fixed readers, handheld readers are easier to deploy and integrate with existing industrial RFID systems and data management tools, with many references available at various price points.
How to find the right handheld RFID reader: A checklist
10 key features to consider when selecting a handheld RFID reader for an asset tracking or inventory management system:
1- How rugged? IP and shocks
The reader should be durable enough to withstand the harsh conditions of industrial and commercial environments. It should withstand drops, water and dust exposure, and temperature extremes. Look for an RFID reader with an IP rating of at least IP54.
2- Connectivity? Stability is better
Common data transfer options include USB, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
3- How much data storage capacity?
Some readers may have limited internal memory, while others may have expandable memory options.
4- With barcodes? Option is available
Some readers come with the ability to scan barcodes and QRcodes.
5- RFID chip? Optimal performance
Companies like Impinj offer chips for both tags and readers (through partners) which ensure optimal performance when associated in the same system.
6- Frequencies? Region-based
RAIN RFID compatibility for the geographic region of operation.
7- Antenna polarisation? Longer range
Linear vs circular polarization.
8- Battery life?
Swapable batteries and charging options such as cradles.
9- Do you need a screen?
RFID tracking system for Manufacturing or Oil & Gas favor industrial RFID readers with a screen/PDA integrated. Readers without a screen are less expensive and can be connected to a mobile phone.
10- Availability?
Lead times have been affected by supply chain issues for even the most established brands.
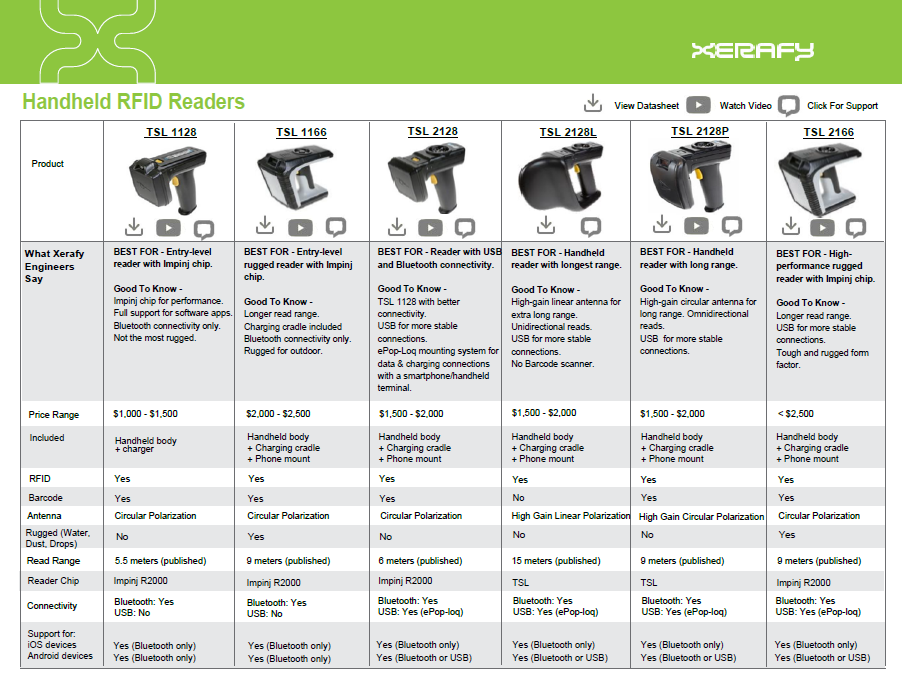
Guide To Handheld RFID Readers
Best-selling, entry-level, and specialized handheld RFID readers, with a focus on durability, read range, and accuracy.
Zebra RFID Readers
Zebra Technologies is a leading global provider of enterprise-level RFID and barcode solutions.
- Wide range of handheld RFID readers and fixed and portal readers.
- Their readers are designed to meet the needs of various industries, including healthcare, retail, and logistics.
- Zebra's readers use advanced technology, such as multi-protocol support and interference rejection, to ensure accurate and reliable tag reading.
- Zebra's readers are integrated with their own software solutions, which help users manage their RFID data and analytics.
- Zebra Technologies is known for its high-quality and durable RFID readers, which can withstand harsh environments and heavy usage.
In addition to their RFID offerings, Zebra is also a major player in the barcode market, offering a wide range of barcode scanners and printers. Their scanners use advanced imaging and decoding technologies to capture barcode data quickly and accurately, making them ideal for high-volume applications.
TSL RFID Readers
- Specialized range of handheld RFID readers designed for asset tracking, inventory management, and access control.
- TSL's handheld RFID readers use advanced technology, such as Bluetooth connectivity and multi-tag reading, to provide accurate and reliable tag detection.
- Their readers are compact and lightweight, making them easy to use and carry around.
- TSL offers a variety of accessories and software solutions that are compatible with their readers, allowing users to customize their RFID system according to their specific needs.
- TSL handheld RFID readers are known for their durability and long battery life, making them suitable for use in challenging environments and prolonged usage.
AsReader RFID Readers
- AsReader is a Japan-based company that specializes in handheld RFID readers, designed for various applications such as inventory management, logistics, and retail.
- Their readers are compatible with iOS devices, allowing users to use their smartphones or tablets as RFID readers.
- AsReader's readers use advanced technology, such as high-frequency antenna and automatic filtering, to provide fast and accurate tag detection.
- The RFID readers are compact and easy to use, making them ideal for mobile applications and field work.
- AsReader offers a range of software solutions, such as cloud-based data management and analytics tools, to complement their handheld RFID readers and provide end-to-end solutions for their customers.
Apulsetech RFID Readers
- A South Korean company that specializes in handheld RFID readers, designed for various applications such as inventory management, asset tracking, and access control.
- The handheld RFID readers use advanced technology, such as multi-protocol support and interference rejection, to provide fast and accurate tag detection.
- Apulsetech's readers are compact and lightweight, with ergonomic designs for comfortable use and easy handling.
- The RFID readers are compatible with Android devices, allowing users to use their smartphones or tablets as RFID readers.
- Apulsetech offers a range of software solutions, such as cloud-based data management and analytics tools, to complement their handheld RFID readers and provide end-to-end solutions for their customers.
Chainway RFID Readers
- Chainway is a China-based company that offers a range of handheld RFID readers for various applications, such as asset tracking, inventory management, and logistics.
- Their handheld RFID readers use advanced technology, such as UHF and high-frequency antenna, to provide accurate and reliable tag detection.
- Chainway's readers are designed for rugged use, with durable construction and IP ratings for water and dust resistance.
- The RFID readers are compatible with Android and Windows devices, allowing users to use their smartphones, tablets, or PCs as RFID readers.
- Chainway offers a range of software solutions, such as cloud-based data management and analytics tools, to complement their handheld RFID readers and provide end-to-end solutions for their customers.
Hopeland RFID Readers
- Hopeland is a China-based company that specializes in handheld RFID readers for various applications, such as warehouse management, asset tracking, and inventory management.
- Their handheld RFID readers use advanced technology, such as UHF and high-frequency antenna, to provide fast and accurate tag detection.
- Hopeland's readers are designed for rugged use, with durable construction and IP ratings for water and dust resistance.
- The readers are compatible with Android and Windows devices, allowing users to use their smartphones, tablets, or PCs as RFID readers.
- Hopeland offers a range of software solutions, such as cloud-based data management and analytics tools, to complement their handheld RFID readers and provide end-to-end solutions for their customers.
FAQs Handheld RFID readers
What is the read range of a handheld RFID reader?
The read range of a UHF RFID handheld reader can vary depending on several factors, such as the tag type, environment, and reader power. Typically, UHF RFID handheld readers can read tags from a few centimeters to several meters.
How to extend the range of a handheld RFID reader?
The read range of a handheld RFID reader can be extended using a combination of these parameters:
Power: More power means more range with power in handheld readers is limited by the battery, whereas fixed readers have higher power output.
Antenna polarization: Linear polarization achieves longer ranges than circular polarization.
Tags: Read range can be extended by optimizing a tag’s position on the asset, orientation (same plane as the antenna), and bonding/attachment (e.g. on metal).
What is the battery life for a handheld reader?
The battery life for a handheld reader can vary depending on the specific model and usage. Some models may have a battery life of a few hours, while others can last up to 10 hours or more.
What RFID antenna polarization is best suited for asset tracking?
A linear polarized antenna is a common type used for RFID inventory tracking and for industrial assets, where the reader antenna transmits RF waves in one level, horizontal or vertical. It is suitable for reading tags in a single orientation and offers a longer read range than circular polarized antennas.
With a circular polarized antenna, the RF waves are transmitted in a circular movement, clockwise or counterclockwise. It offers a broader read field than linear polarized antennas, making it suitable for reading tags in different orientations. However, the read range may be slightly shorter.
Additionally, fixed RFID readers can use near-field or far-field antennas from manufacturers such as Times7 or MTI Wireless. Near-field antennas are designed for reading tags at close range, indoor, on small items or in tight spaces. Far-field antennas are designed for reading tags at longer ranges, typically up to several meters.
Can I use an RFID reader on iPhone?
Yes, a limited number of handheld RFID readers support iOS. The external UHF reader requires a USB or Bluetooth connection to for reliable and accurate readings of RAIN RFID tags.
An NFC-enabled iOS or Android mobile phone can read NFC tags, a type of high-frequency RFID. The phone has a built-in Near Field Communication (NFC) chip that allows them to communicate with other NFC-enabled devices. The range of NFC reading is typically limited to a few centimeters.
What is an RFID Reader Writer?
All RFID Readers can both read and write data. Writing data is possible using specialized Read Write RFID tags, which contain an RFID chip featuring additional memory banks.
RFID systems for inventory management and asset tracking often necessitate writing data to RFID tags. Unique identification numbers, location information, and usage data are some examples. Other tracking systems, such as access control or product tracking, do not usually necessitate the modification of the data recorded on the tags.
With limited data entry capabilities, handheld RFID readers will find it difficult to write data to more than a few tags. A dedicated RFID reader writer can write large volumes of data rapidly and efficiently. Examples include RFID modules embedded into complex industrial processes, desktop RFID programmers with associated software, and RFID printers used for asset labeling in the field.
What is an RFID scanner?
An RFID scanner is an RFID reader that features an additional optical module to read barcodes and QRcodes.
Unlike the RFID reader that can read multiple tags simultaneously and at distance, the barcode scanner still requires a clear line-of-sight and is limited to individual readings.
What is the difference between RFID and barcode technology?
RFID scanners and barcode technology have distinct differences in terms of their functionalities. The key disparity lies in the need for human intervention, often referred to as “line of sight.” This concept pertains to the proximity between the operator and the labeled or tagged item being scanned or read.
In the case of barcode technology, operators must position their handheld scanners within the line of sight of the item to obtain an accurate read. This means that the operator needs to be physically close enough to visually observe and scan the barcode. On the other hand, RFID technology allows operators more flexibility by eliminating the limitation of line of sight. To collect data using RFID, operators only need to be within the range of the RFID tag. This means that they can gather data for any item within the read range without requiring physical proximity or direct visibility of the tag itself.
Moreover, RFID technology offers the advantage of reading multiple items simultaneously within its read range. This capability allows for efficient data collection without the need for operators to move from shelf to shelf physically. Conversely, barcode technology necessitates manual scanning of each individual item with the handheld scanner, making it a more time-consuming process when dealing with multiple items.
Which RFID tags to use with RFID UHF readers?
RAIN RFID tags from reputable manufacturers will fully operate with RFID UHF readers.
RFID tags selection will depend on the specific application and requirements, with size, read range, durability, and environment among the most critical factors to be considered.
It is important to choose tags that are compatible with the handheld reader and can be easily integrated into the existing RFID system.